 Terratec bringt mit dem Cinergy T2 Stick Micro eine DVB-T2-Empfangslösung für den Windows-PC und Android-Geräte. Der Empfänger wird über Micro-USB oder USB angeschlossen und überträgt das digitale TV-Programm des Antennenfernsehens mit einer Auflösung von bis zu 1080p. (DVB-T, H.265)
Terratec bringt mit dem Cinergy T2 Stick Micro eine DVB-T2-Empfangslösung für den Windows-PC und Android-Geräte. Der Empfänger wird über Micro-USB oder USB angeschlossen und überträgt das digitale TV-Programm des Antennenfernsehens mit einer Auflösung von bis zu 1080p. (DVB-T, H.265) Month: June 2016
Senkrechtstarter: Google-Mitgründer Larry Page investiert in fliegende Autos
Die Startups Zee-Aero und Kitty Hawk arbeiten an fliegenden Autos. An beiden Unternehmen soll Google-Gründer Larry Page Anteile halten. Auch andere Firmen versuchen teilweise seit Jahren und oft vergeblich, Flugautos in die Luft zu bringen. (Flugauto, Technologie)
 Die Startups Zee-Aero und Kitty Hawk arbeiten an fliegenden Autos. An beiden Unternehmen soll Google-Gründer Larry Page Anteile halten. Auch andere Firmen versuchen teilweise seit Jahren und oft vergeblich, Flugautos in die Luft zu bringen. (Flugauto, Technologie)
Die Startups Zee-Aero und Kitty Hawk arbeiten an fliegenden Autos. An beiden Unternehmen soll Google-Gründer Larry Page Anteile halten. Auch andere Firmen versuchen teilweise seit Jahren und oft vergeblich, Flugautos in die Luft zu bringen. (Flugauto, Technologie) Akku-Update: Tesla Model S wird günstiger
Tesla Motors hat mit dem Model S 60 ein neues Einsteigermodell seines Elektroautos vorgestellt, das mit einem 60-kWh-Akku und Heckantrieb ausgerüstet und daher vergleichsweise günstig ist. Gegen Aufpreis schaltet Tesla beim Akku auch 75 kWh nachträglich frei. (Tesla Motors, GreenIT)
 Tesla Motors hat mit dem Model S 60 ein neues Einsteigermodell seines Elektroautos vorgestellt, das mit einem 60-kWh-Akku und Heckantrieb ausgerüstet und daher vergleichsweise günstig ist. Gegen Aufpreis schaltet Tesla beim Akku auch 75 kWh nachträglich frei. (Tesla Motors, GreenIT)
Tesla Motors hat mit dem Model S 60 ein neues Einsteigermodell seines Elektroautos vorgestellt, das mit einem 60-kWh-Akku und Heckantrieb ausgerüstet und daher vergleichsweise günstig ist. Gegen Aufpreis schaltet Tesla beim Akku auch 75 kWh nachträglich frei. (Tesla Motors, GreenIT) Moto Mods: Das Smartphone als Elektronik-Steckbrett
Lenovo stellt für sein neues, modulares Smartphone Moto Z ein offenes Entwicklerkit vor, um eigene Module zu entwickeln. Wem es an Elektronikwissen oder Lötfähigkeiten mangelt, kann auch Aufsätze für den Raspberry Pi nutzen. (Smartphone, Lenovo)
 Lenovo stellt für sein neues, modulares Smartphone Moto Z ein offenes Entwicklerkit vor, um eigene Module zu entwickeln. Wem es an Elektronikwissen oder Lötfähigkeiten mangelt, kann auch Aufsätze für den Raspberry Pi nutzen. (Smartphone, Lenovo)
Lenovo stellt für sein neues, modulares Smartphone Moto Z ein offenes Entwicklerkit vor, um eigene Module zu entwickeln. Wem es an Elektronikwissen oder Lötfähigkeiten mangelt, kann auch Aufsätze für den Raspberry Pi nutzen. (Smartphone, Lenovo) In rodents fed high-fat diets, gut microbes boost hunger, trigger obesity
Bacteria-made acetate signals vagus nerve, sparking hunger hormone, insulin resistance.

(credit: Joanna Servaes)
After several hints that gut microbes may be key players in the obesity epidemic, a new study provides a mechanistic explanation of how the intestinal inhabitants directly induce hunger, insulin resistance, and ultimately obesity in rodents.
After mice and rats were fed a high-fat diet, their gut microbes produced more acetate, a short-chain fatty acid made during bacterial fermentation. That acetate spread throughout the rodents’ bodies and into their brains where it activated the parasympathetic nervous system. This system, largely involving the vagus nerve, controls the body’s unconscious actions, such as digestion, excretion, and sexual arousal. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, the microbe-made acetate spurred the rodents to produce more insulin, a hormone made by pancreatic β-cells that promotes calorie storage, as well as ghrelin, a hormone involved in hunger. The result was rodents that ate more developed insulin resistance—a precursor to diabetes—and became obese, the researchers report in Nature.
“This generates a positive feedback loop,” the authors conclude—which makes sense for foraging animals, they add. If a foraging animal stumbles upon a calorie-dense food in the wild, it would be advantageous if their gut signaled their brain to keep eating and store some energy, stocking up to survive leaner times. “However, in the setting of chronic exposure to calorically dense, abundant food, this gut microbiota–brain–β-cell axis promotes obesity and its related sequelae of hyperlipidaemia [high levels of lipids in the blood], fatty liver disease and insulin resistance,” the authors write.
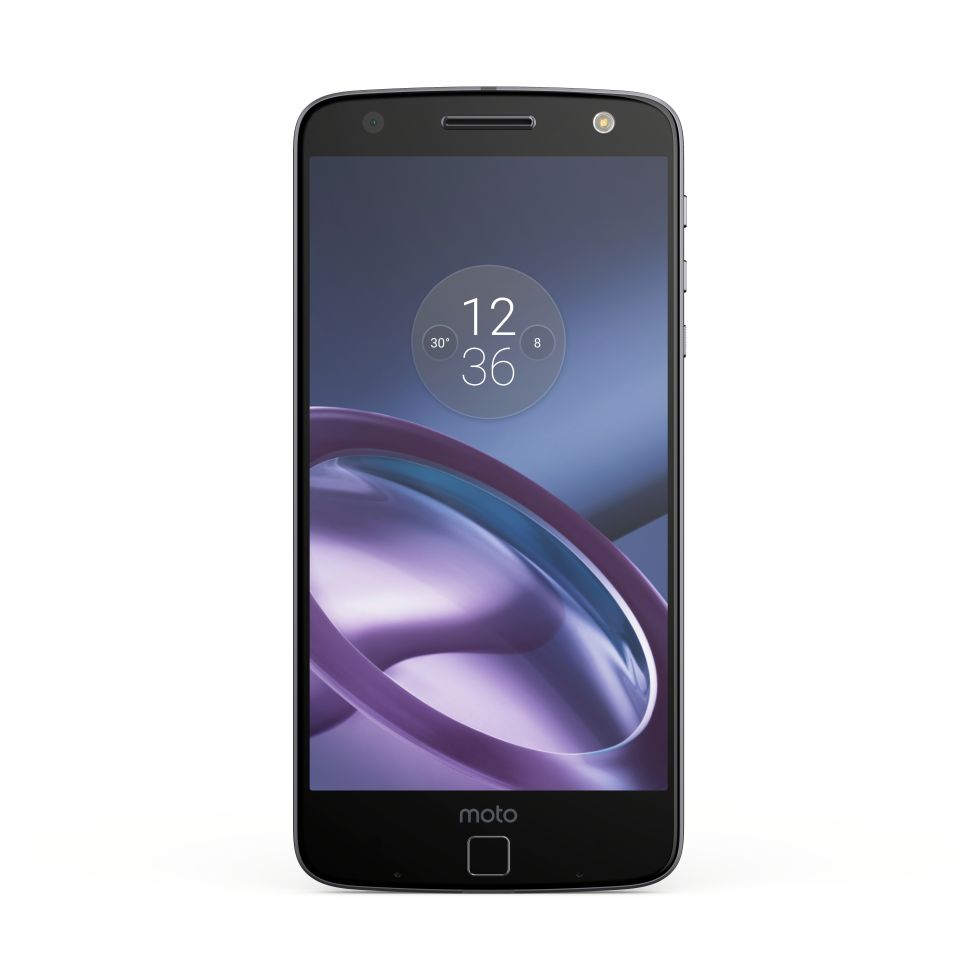
Meet Motorola’s new flagship, the modular Moto Z
The Moto Z lets you snap on backpacks with extra functionality.
Today, Motorola took the wraps off its 2016 flagship, the Moto Z. These phones (there are two of them) are markedly different from past Moto flagships, which is appropriate since the Moto Z represents Motorola's transition from "A Google Company" to Lenovo subsidiary. The actual deal closed over a year ago, but product pipelines mean only now are we seeing Lenovo's full influence.
The Moto Z is a metal phone the company is calling "the world's thinnest premium smartphone." It has a 5.5-inch, 1440p AMOLED display, a Snapdragon 820, 4GB of RAM, and 32 or 64GB of storage with a MicroSD slot. For cameras, there's a 13MP rear sensor with OIS and laser autofocus and a 5MP front camera with a wide angle lens. Other extras include a fingerprint sensor, "water-repellant coating," and a front flash.
Lenovorola hasn't said how big the battery on the Moto Z is, only that it will get "30 hours" of battery life.
No more Mr. Nice Ubisoft: First-time Division cheaters now banned permanently
Stricter punishments come amid claims of improved cheat detection tools.

Instead of fighting through this wasteland, cheaters will now have to face the wasteland of their own lives.
In a move intended to help stem a wave of cheating in the online portions of The Division, Ubisoft says it is rescinding its policy of issuing 14-day suspensions when a player is first detected using a cheat engine. Now, those players will be permanently banned when found.
The new policy comes after The Division team said it became clear to them that the 14-day suspension policy currently in place "has not been dissuasive enough... judging from your feedback, and based on what we witnessed when cheaters came back to the game." That 14-day suspension policy was itself an increase from the previous three-day suspensions that were given out for first offenses until late April.
Those temporary suspensions certainly didn't seem to be discouraging cheaters very much, according to widespread reports of cheating and exploit use in the game. "The message is out," one player wrote on The Division forums in April. "Cheat all you want, it will take forever to catch you apparently, and you get to keep all the exp/money/items you gained and then after a three-day suspension you get to laugh, come back in, and reap your reward. Then just don't cheat anymore."
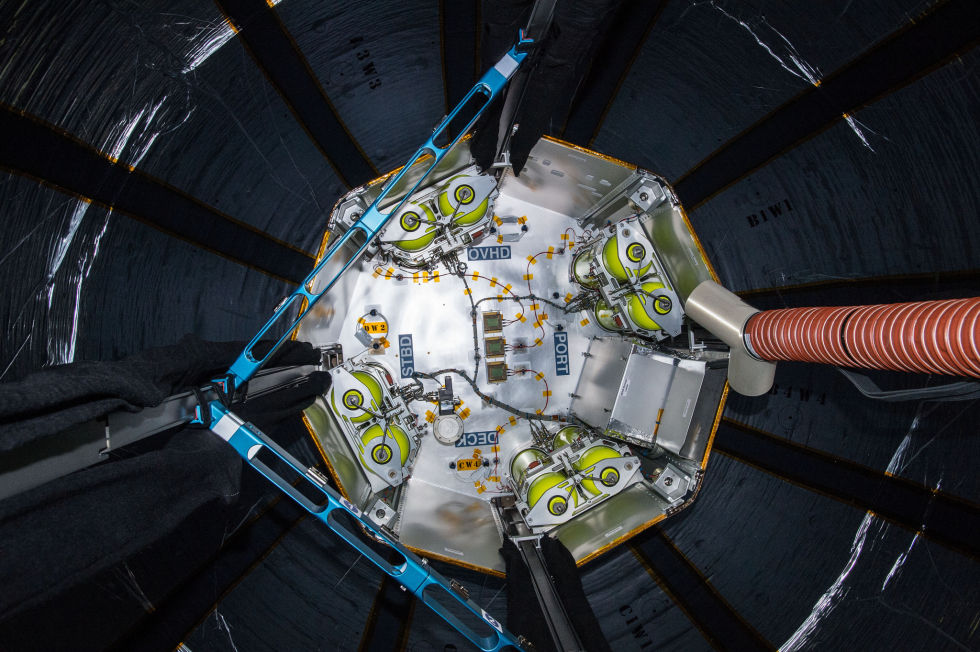
NASA’s room in space has expanded, but will it prove durable?
New images provide the first high-def look into Bigelow’s expandable module.
NASA
The interior of the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module is seen during sensor installation and after successful expansion. This is the best view we've seen so far.
10 more images in gallery
In April, astronauts attached an expandable room to the International Space Station, which they successfully inflated at the end of May. This week, NASA astronaut Jeff Williams entered the Bigelow Aerospace expandable module and said everything was fine. He subsequently installed some sensors to monitor air pressure, temperature, and other variables, as well as other hardware.
Finally, on Wednesday, Williams removed his tools from the module and closed the hatch. Astronauts will not reenter the 13-foot-long module now until August, when they will perform more checks of the equipment.
Why wait so long? Because as important as it was to demonstrate the module could be expanded, it is more important still to prove its durability over the two-year experiment. Engineers with Bigelow have said the expandable’s kevlar-like weave should be at least as protective as the station’s aluminum hull when it comes to tiny orbital debris. The company also says that with this material, the interior of the module should prove a quieter location than the notoriously noisy station interior. NASA is also interested in how the non-metallic shell of the module limits radiation exposure.
Google Fiber-free? Alphabet wants to deliver gigabit internet without wires
Google Fiber offers high-speed internet service to customers in select US markets… and when I say high-speed, I mean Google Fiber is one of the fastest internet service providers in the country, with speeds up to 1 gigabit (1,000 Mbps) for both downloads and uploads.
But part of the reason Google Fiber is only available in 5 markets at the moment is because it takes a lot of work to build out a fiber optic network.

Google Fiber offers high-speed internet service to customers in select US markets… and when I say high-speed, I mean Google Fiber is one of the fastest internet service providers in the country, with speeds up to 1 gigabit (1,000 Mbps) for both downloads and uploads.
But part of the reason Google Fiber is only available in 5 markets at the moment is because it takes a lot of work to build out a fiber optic network.
Four new elements get their final names
Good luck pronouncing the proposed names for elements 113, 115, 117, and 118.
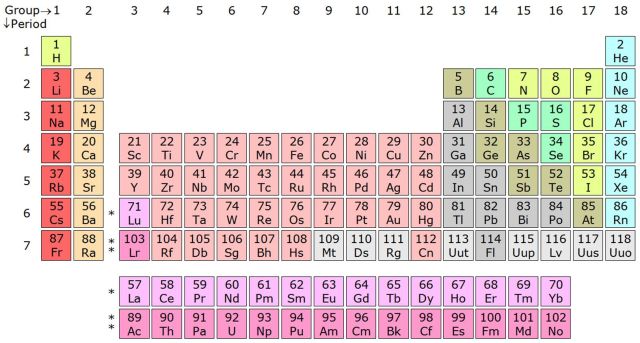
Wikipedia is behind the times. All those elements that start with "Uu" in the lower right? They've got real symbols now. (credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Earlier this year, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) accepted the evidence that indicated we had produced four new elements, filling out the bottom row of the periodic table. At the time, they were given temporary names—and catchy ones, too. We'll all be sad to see ununseptium (element 117) go, but you'll be glad to know that the formal names are probably just as difficult to pronounce properly.
Three of the new names honor the places where the elements were produced; the fourth recognizes a key person who helped organize the work involved.
For element 113, Japan is recognized by one of its alternate names, Nihon. The element will be called nihonium, and bear the symbol Nh. The remaining elements were produced by collaboration between the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Russia and two of the US' national labs: Oak Ridge and Lawrence Livermore. Element 115 honors the Russian part of that collaboration with the name moscovium (symbol Mc). 117 handles Oak Ridge by getting the name tennessine, or Ts. Lawrence Livermore has the misfortune of being in California, which already has an element named after it, so it gets left out.

